How to make our computer system secured Cybersecurity ǀǀ Updates 2020 ǀǀ Types of Attacks & Hacks
What is Computer Security?
Technology is growing every day with 44% of tech spend in 2020 in comparison to 38% in 2019(source: spiceworks). As it grows, it transforms our digital world noding towards a complete digitalism in near future. Internet use is increasing exponentially with 4.5 Billion of world's population is Online already, and this accounts for 60% of human population on our dear planet Earth. This often corresponds to more vulnerability to cyber-attacks.
Computer security deals with the protection of computer systems and information from alter, theft, data manipulation and unauthorized use. The main reason users get attacked frequently is that they lack adequate defenses to keep out intruders, and cyber criminals. Computer security ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of your computer system and their stored data.
Why Users Get Attacked?
Main motives for attacking a computer system are:-
- Disrupting a business’ continuity: If a business is disrupted, it causes great harm to the organization in the form of lost profits, fraud, and damage to its reputation.
- Information theft and manipulating data: Hackers take confidential information that they steal from organizations and sell it to individuals or groups on the black market.
- Creating chaos by disrupting critical infrastructure: Cyber terrorists attack a company or a government body to disrupt their services, doing damage that can potentially affect an entire nation.
- Propagating religious or political beliefs: Hackers may infiltrate websites to promote religious dogma or a certain political agenda, usually to sway voters to vote a certain way.
- Financial loss to the target: Hackers attack an organization or business and disrupt their services in such a way that the target has to allocate substantial funds to repair the damage.
- Demanding ransom: The hackers employ ransomware to block a website or servers, releasing control only after a ransom is paid.
- Achieving a state’s military objectives: Rival nations continuously keep an eye on each other and sometimes employ cyber criminal tactics to steal military secrets.
- Damaging the reputation of target: The hacker may have personal reasons to attack an organization or individual so that their reputation suffers.
Types of Attacks:-
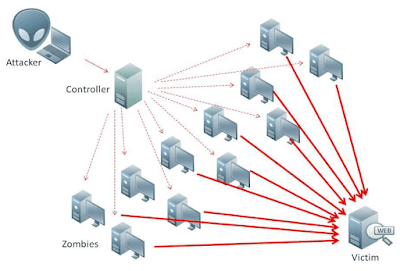
1. Denial of service (DDoS): DDoS is an attack used to restrict the user’s access to the system resources by flooding the server with useless traffic. The botmaster commands all the bots to access a resource at the same time so that the resource gets jammed up. Then, if a genuine user wants to access that same resource, he will not be able to do so.
Fig: Denial of service illustration (Credit : www.lifars.com)
2. Malware attack: This is a malicious program that disrupts or damages the computer. There are four main types of malware:-
- Keylogger: Keylogger records all the keystrokes on the targeted keyboard. Most hackers use it to get pins, passwords and account details.
- Virus: A computer virus is a malicious code that replicates by copying itself to another program or document and changes how a computer works. For example, trojan virus, Zeus virus, Melissa virus etc.
- Worms: This is a standalone program that runs independently and infects the system. One of the more popular example is W32.Alcra.F. The worm propagates itself through network share devices.
- Trojan horse: This is a malicious code that takes over your computer. This code can damage or steal information from your computer.
3. Man in the middle: Say, for example, you want to do an online transaction. You connect to your bank and conduct the payment. Simple, right? This is illustrated in the below image:
Fig: Man in the middle attack (credit: www.phoenixnap.com)
Now, while you are doing a transaction, you have to enter the details of your card and the PIN. The cyber attacker spoofs you and monitors your transaction. As soon as you enter your details, he will have access to all of that information, as shown in the below image:
4. Phishing: The attacker sends bait, often in the form of an email. It encourages people to share their details. For example, you get an email like this:
Fig.: Phishing (credit: www.duocircle.com)
If someone is a customer of ABC bank, he would probably open the link and enter the details. But these kinds of emails are always phishing. Banks do not send emails like this.
5. Eavesdropping: Attacker observes traffic on your system and the work you are doing. The attacker can monitor you in three ways:
- Email monitoring
- Which websites you visit
- What items you download
6. SQL injection: As the name suggests, an SQL injection vulnerability allows an attacker to inject malicious input into a SQL statement. This type of attack happens only on websites. The best example would be www.facebook.com. There is a database stored on the facebook website. The hackers get into that database and sign in using someone else's username and password.
7. Password attack: To crack a password or find a password, hackers employ these following techniques:
- Dictionary attack: In this method, they handle every password that is possible through the dictionary.
- Rainbow table: There are rainbow tables that contain precomputed hash values. Attackers use this table to find the user’s password.
- Shoulder surfing: The attackers observe the user’s keyboard by looking over the user’s shoulder.
- Keylogger: As the name suggests, keylogger records all the hits on the keyboard. Most people use it to get passwords and account details
- Brute force: It is a trial and error method used to decode the password or data. This attack takes the most amount of time.
8. Social engineering: Attackers create social situations that encourage you to share your password. For example, let’s say that you are out of your office, and you get a call. The person says that he is from the IT department and they have found out that your system has been compromised. He asks you to share your password. You might believe him and share your password. However, the caller was, in fact, a hacker, and how he has your password. Now that he has access, he can compromise your organization's data. The best way to avoid the effects of social engineering is to learn your organization’s protocol regarding password sharing.
What to Secure?
- Confidentiality: The principles of confidentiality assert that information and functions can be accessed only by authorized parties. Example: military secrets.
- Integrity: The principles of integrity assert that information and functions can be added, altered, or removed only by authorized people and means. Example: incorrect data entered by a user in the database.
- Availability: The principles of availability assert that systems, functions, and data must be available on-demand according to agreed-upon parameters based on levels of service.
How Do You Secure Your Computer?
1. Two-way authentication: Two-factor authentication adds a layer of security to the authentication process by making it harder for attackers to gain access to a person's devices or online accounts. For example, when you make online payments, you first have to confirm your card’s cvv number, then you undergo a second confirmation by providing your mobile number.
2. Secure passwords: Create strong passwords so that no one will be able to hack or guess your password. The best passwords include:
- At least 15 characters.
- Capital letters.
- Numbers.
- Special characters. Example: @#$%.
3. Regular updates: Always keep your system and all its software updated. Many updates contain additional defenses against cyber attacks.
4. Antivirus: Antivirus is a computer program used to prevent, detect, and remove malware. Examples of antivirus include Norton, Quick Heal, and McAfee.
5. Firewalls: Firewalls prevent unauthorized Internet users from accessing private networks connected to the Internet, especially intranets.
6. Anti-phishing tactics: When you get an email that looks suspicious or has no relation to you, then do the following:-
- Do not click on the link in the email.
- Do not open the attached files.
- Do not provide any personal details if asked.
7. Encryption: This is the process of converting ordinary plain text into unintelligible text and vice-versa. Encryption is used in many applications like:-
- Computer passwords.
- E-commerce transactions.
- Banking transactions.
Unfortunately, cybercrime is increasing daily, so it’s imperative to have a solid grasp of the best cyber security practices. While the internet is transforming and improving our lives, the vast network and its associated technologies have become a lucrative hunting ground for a growing number of cyber criminals, agents from which individuals and businesses must protect themselves.
The consequences of these attacks can range from the ruin of a business to the crashing of a national economy. Confidential or sensitive data can be lost, privacy violated, and reputations ruined. Your computer could even be used by a hacker to attack other computers, which in turn could send the authorities looking for you!







0 comments:
Post a Comment